Electroplating
Plating (Electroplating) is a process that utilizes electrolytic principle to deposit a thin layer of other metal or alloy on surface of parts, to prevent metal from oxidation (rust), improve the wear resistance and electric conductivity, reflective resistance, corrosion resistance, copper sulfate, etc, and better aesthetics, and so on.
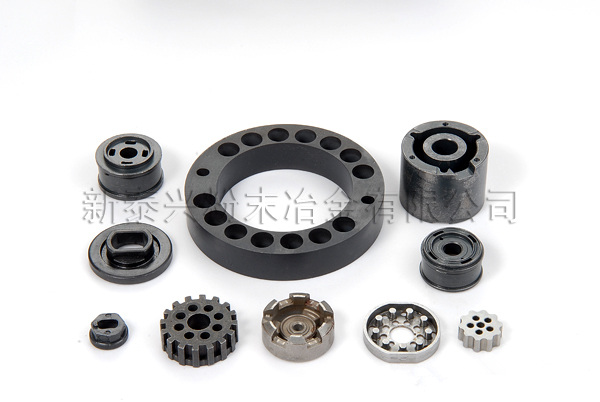
On Fe-based Powder Metallurgy Prodcuts
Surface of iron-based powder metallurgy produts is porous, and the interior consists oil. So the parts are easily permeated by acid, alkali solution and plating solution, and cause flooding point after plating, when subjected to conventional plating pretreatment, then are corroded from inside to ouside, and then lose coating protection. Therefore, the pretreatment before plating of iron based powder metallurgy produts are pretty difficult. Manufacturers must adopt special method to obtain the excellent coating performance. In general, there are three methods to improve the quality of electroplating on Fe-based powder metallurgy parts: hole sealing, such as hole sealing in boiled distilled water, hole sealing in paraffin with high melting point, hole sealing filled by zinc stearate and hole sealing in silicone oil, etc; Intermediate coating, such as iron, cyanide copper plating and electroless nickel plating, for subsequent coating base; Direct plating method.
Oxidative Blacknening
Besides, oxidative blackenning treatment can effectively improve rust resistance of parts. Normally, there two methods of blackening on powder metallurgy iron based products, one is direct oxidative blackening; The other is blackening finishing on surface plated with coppe.



 English
English German
German Spanish
Spanish French
French Italian
Italian Portuguese
Portuguese Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Russian
Russian Chinese
Chinese NO.2 Machinery
NO.2 Machinery NO.2 Machinery
NO.2 Machinery SINTS
SINTS